For indoor growers, it is critical to maximize productivity using limited resources and space, while keeping costs at a minimum. If you don’t understand how CO2 supplementation influences photosynthesis and plant growth, you’re limiting the productivity and profitability of your operation.
This guide helps indoor plant growers and greenhouse owners easily and effectively improve plant productivity and quality by understanding how CO2 enrichment influences plant growth, and how it interacts with the driving force behind plant transpiration: VPD.
Quick Summary
- Higher CO2 concentrations increase the ideal temperature for photosynthesis.
- During photosynthesis, plants absorb both water and CO2 from the soil and air, but as temperatures increase, VPD increases, stomata close, and the uptake of CO2 is reduced, causing plant stress. As a result, it is critical for growers to maintain ideal VPD levels at higher temperatures.
- To achieve optimal VPD at higher temperatures, humidity levels must be increased.
- At higher humidity levels, there is a greater risk of plants getting diseases (bud rot, powdery mildew, etc.) and pests, which need to be managed.
- To take advantage of increased CO2 levels, maintain optimal VPD by increasing relative humidity while managing pest and disease risk.
What CO2 Does for Plants
- CO2 is used for photosynthesis, the process that plants use to produce energy in the form of glucose. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs light into a plant’s cells, which helps synthesize nutrients from water and CO2. Oxygen is released back into the air, and CO2 is transformed into glucose, a sugar molecule which provides plants with fuel to grow.
- Chemical reactions occur during photosynthesis. The main chemical reaction is 6CO2 + 6H2O + light yields C6H12O6 + 6O2. This means that carbon dioxide + water + light yields glucose + oxygen.
- Studies have been conducted analyzing the effects of higher temperatures and CO2 concentration with the yield of increased crop growth. Higher concentrations of CO2 have been found to increase healthy plant growth.
- A study was conducted to determine the effects of higher CO2 concentration and the cultivation of Japanese rice. Crop yields increased for all five different cultivators studied, ranging from 3.4% to 30.3%.
- Another study compared the net rate of photosynthesis in tomato plants at different CO2 concentrations and different light intensities. The results determined that both net photosynthesis and optimal growing temperature increase dramatically with an increase in CO2 concentration regardless of light intensity.
- A different study compared the effect of elevated CO2 concentration and higher temperature on potato crop yields. This study concluded that although elevated temperatures alone can negatively influence the growth of potatoes, a higher CO2 concentration in conjunction with higher temperatures promotes healthier production and better quality of potato crops.
How Does Photosynthesis get Influenced by CO2
CO2 is an essential component of photosynthesis. This is important for greenhouse production that aims to optimize crop yield. For the majority of greenhouse crops, increasing CO2 levels to 1000 ppm (parts per million) results in an increase in photosynthesis by 50% over ambient CO2 levels.
A scientific study was conducted to determine the effects of elevated CO2 concentration on photosynthesis with a perspective on root sugars. The study concluded that the production of carbohydrates was increased in plants grown under conditions with higher CO2 concentration due to an increase in photosynthesis. The plants also produced more sucrose (sugar) which regulates nutrient acquisition. This study provides insight about positive changes that could occur in plant roots grown in conditions with higher CO2 concentration.
The enzyme Rubisco, short for Ribulose-1,5 -bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, is an abundant enzyme that is involved in carbon fixation. Carbon fixation is a process by which CO2 in the atmosphere is converted during photosynthesis to form glucose.
Another study examined how Rubisco catalyzes photosynthentic reactions involving O2 and CO2 gases. The results determined that, at equal concentrations of the gases, Rubisco binds CO2 stronger than it does O2. This suggests that this enzyme can act as a reservoir for CO2 storage.
This finding is significant because it provides insights on how to reduce plant stress due to elevated temperatures. Increasing CO2 concentration can improve Rubisco efficiency. This in turn helps build resilience in crops and improve yield at higher temperatures.
How Much CO2 do Plants Need
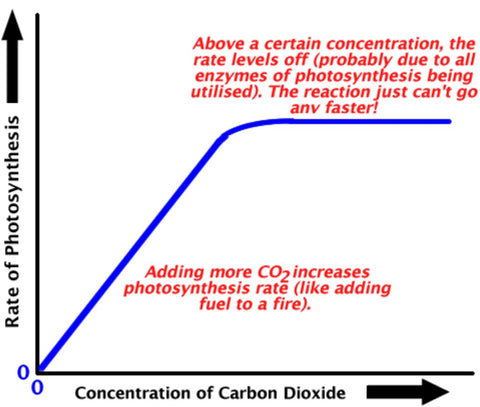
- Average outdoor CO2 levels are normally around 400 ppm, which achieves normal outdoor plant growth.
- Greenhouse and indoor plants grow better with CO2 concentration of at least two to three times that of outdoor levels (800 to 1200 ppm).
- CO2 levels above 2000 ppm are toxic to plants, and most experts agree that 1500 ppm is the maximum CO2 level for maximum plant growth.
The Relationship Between CO2 and Ideal Photosynthesis Temperature
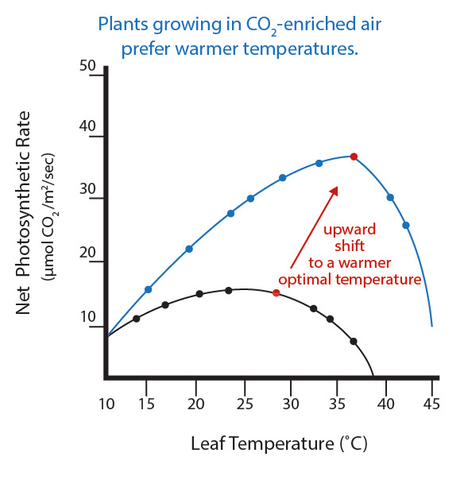
The rate of photosynthesis increases as temperature increases. The optimal temperature for photosynthesis, however, is dependent on CO2 concentration.
A scientific study about CO2 examined the net photosynthesis rate of big tooth aspen leaves growing under two different CO2 concentrations at various temperatures.
- At a low CO2 saturation of 325 ppm, optimal growing temperature was around 25 degrees Celsius.
- At 1935 ppm of CO2, the net photosynthetic rate was boosted by 450% at an optimal growing temperature of 36 degrees Celsius.
- It was also determined that the transition from life sustaining to life depleting conditions in this plant species occurs at around 39 degrees Celsius.
Conclusion
- When supplementing CO2, plants grow bigger and faster, but need higher temperatures and humidity to really take advantage of the higher CO2 levels.
- Growers can greatly improve yields by leveraging this knowledge about how CO2, Temperature and VPD interact. To really see how these forces influence your garden, you need to have an accurate and reliable way to monitor their parameters.
- Pulse Pro monitors CO2, VPD, temperature, humidity, PAR and other key agricultural data types, and helps you keep track of and optimize the environment. It makes growing plants indoors safe, simple, and worry-free for growers of any size.
References / Further Reading
Take a look at this article on how to track CO2 concentration and VPD levels for optimal plant growth.



![[Feature Highlight] Zones w/ Batch & Phase Tracking - Pulse Grow](http://pulsegrow.com/cdn/shop/articles/feature-highlight-zones-w-batch-phase-tracking-726407_1600x.png?v=1695824155)
